
Calcium Phosphate - Ca3(PO4)2
What is Calcium Phosphate?
Calcium phosphate is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with a chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as Calcium phosphate tribasic or Tricalcium Phosphate.
Calcium phosphate appears as a white amorphous or crystalline powder that is odourless and tasteless. It is insoluble in ethanol, and acetic acid but soluble in dilute nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It slightly dissolves in water. It is found in bones, milk, teeth, and ground.
Table of Content
- Preparation
- Properties
- Ca3P2 + H2O
- Calcium Phosphate Solubility
- Structure
- Uses
- Occurrence
- Health Hazards
- Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs
Apatite is a mineral rock which is an impure and complex form of calcium phosphate which produces tribasic calcium phosphate. Apatite is a form of phosphorite which contains calcium phosphate mixed with other compounds.
Calcium phosphates are important materials in biology, geology, industry, medicine and dentistry. Its formation, functions and applications depend on its structure, composition, solubility and stability.
Preparation of Calcium Phosphate
It can also be produced by reacting phosphoric acid (H3PO4) with solid calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2
Ca(OH)2+H3PO4→Ca3(PO4)2+H2O (unbalanced)
3Ca(OH)2+2H3PO4→Ca3(PO4)2+6H2O (balanced equation)
Dibasic calcium phosphate can be produced in the former of these reactions by using an aqueous solution of calcium hydroxide. Monobasic calcium phosphate is obtained by adding excess phosphoric acid to either a dibasic solution or a tribasic calcium phosphate solution and letting the solution evaporate.
Properties of Calcium Phosphate - Ca3(PO4)2
Ca3(PO4)2 Calcium phosphate Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass 136.06 to 310.20 g/mol Density (tribasic) 3.14 g/cm³ Boiling Point Decomposes Melting Point (tribasic) 1670°CCa3P2 + H2O
Calcium phosphide reacts with water to form phosphane and calcium hydroxide. The chemical reaction is given below.
Ca3P2 + 6 H2O → 2 PH3 + 3 Ca(OH)2
Calcium Phosphate Solubility - Ca3(PO4)2
Solubility is one of the most important characteristics of calcium phosphate salts. It is solubility that defines the course of several reactions involving calcium phosphates such as absorption, precipitation, hydrolysis and phase transformation. Calcium phosphate solubility also plays a major role in biological processes including hard tissue formation and resorption as well as pathological calcification.
Calcium phosphate-based bone graft replacements (mostly tricalcium phosphate or hydroxyapatite) are bioceramics that have the greatest resemblance to bone minerals. This is what makes calcium phosphate excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability and osteoconductivity.
Calcium is a mineral found naturally in food. Calcium is essential for many normal functions of the body, in particular bone formation and maintenance. Calcium can also bind to other minerals (such as phosphate) and help to extract them from the body. Calcium phosphate is used to prevent and treat calcium deficiencies. Calcium phosphate may also be used for purposes not specified in this drug guide.
Solubility is conventionally described as the quantity of a solid that can dissolve into a unit volume of solution. With calcium phosphates, this level also varies by many orders of magnitude, including variations in pH and concentrations of acids and bases, such as HCI and NaOH. Water-soluble calcium phosphate is derived from the skeletons of vertebrate animals. Water soluble calcium phosphate is an important material for plant growth and is commonly dispersed in the soil. Calcium phosphate is insoluble in water but soluble in acids: it is used in natural farming. Calcium phosphate may dissolve slightly in CO2-containing water.
Structure of Ca3(PO4)2
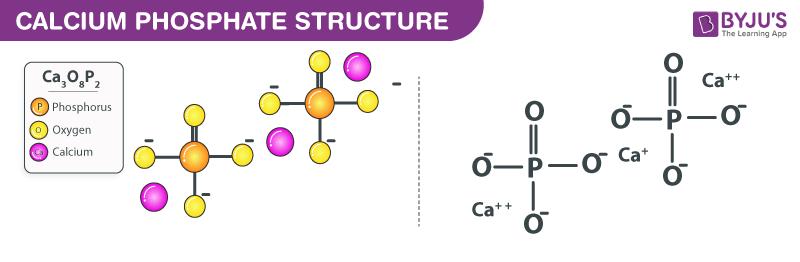
Uses of Calcium phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2)
- Calcium phosphate is used as an antacid and dietary supplement in veterinary medicine.
- It is used in medicine as calcium replenisher.
- It is used as a buffer in food.
- It is used stabilizer in plastics.
- It is used in the manufacturing of milk glass.
- It is used in the production of fertilizers.
- It is used in the manufacture of luminescent materials.
- It is used to clarify sugar syrups.
- It is used in dental powders.
Occurrence of Calcium Phosphate
Calcium and phosphorus make up the bulk of animal mineral nutrient requirements (to fulfill both body tissue and milk needs), hence DCPD is a popular and commonly used animal supplement. Dicalcium Phosphate Dihydrate is also of concern as it is the most soluble of barely soluble calcium phosphate crystals, making it a good choice for rock phosphate dissolution tests. The fate of DCPD in the soil is rather temporary.
Mineral phosphorus is usually applied to soil in a water-soluble form, such as triple super phosphate or diammonium phosphate. As phosphorus dissolves a high concentration of solution P, precipitation reactions are preferred. Calcium phosphates are found in nature in many ways and are the primary minerals for the manufacture of phosphate fertilizers and for a variety of phosphorus compounds.
Health Hazards Associated with Calcium Phosphate
When the toxic doses ingested become more than 2 g/kg unusual skin sensitization occurs. Inhaling it may cause chemical pneumonitis. Calcium phosphate is used in many products in biomedicine, but also in dentistry and cosmetics. In certain situations, it is found in nanoparticle form, either on purpose or after degradation or mechanical abrasion. Possible issues refer to the biological impact of these nanoparticles.
A thorough literature review shows that calcium phosphate nanoparticles, as such, do not have inherent toxicity, but may lead to an increase in intracellular calcium concentration following endosomal uptake and lysosomal degradation. However, cells are able to remove calcium from the cytoplasm within a few hours, unless very high doses of calcium phosphate are used.
The cytotoxicity observed in some cell culture studies , especially for unfunctionalized particles, is likely due to particle agglomeration and subsequent sedimentation on the cell layer, leading to a very high local concentration of particles, high absorption of particles, and subsequent cell death.
Calcium phosphate nanoparticles can reach the bloodstream by inhalation, but no harmful effects have been observed with the exception of extended exposure to high particle doses. Calcium phosphate nanoparticles within the body do not pose a risk because they are normally resorbed and destroyed by osteoclasts and macrophages. Keep visiting us for the latest updates on the chemical compound names. To learn more about the chemical reactions and structural details of Calcium phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2 from the expert faculties at BYJU’S register now!
Read more:
- Chemical compound formula
- Chemical formula
Link nội dung: https://myphamsakura.edu.vn/ca3-po4-2-ra-p-a54727.html